Computed Tomography (CT or CAT) Scan of the Brain
A CT scan, also known as a CAT scan, is a diagnostic imaging test that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to create cross-sectional images of the body. This article will answer some of the most common questions people have about CT scans of the brain.
1. What is a CT scan of the brain?
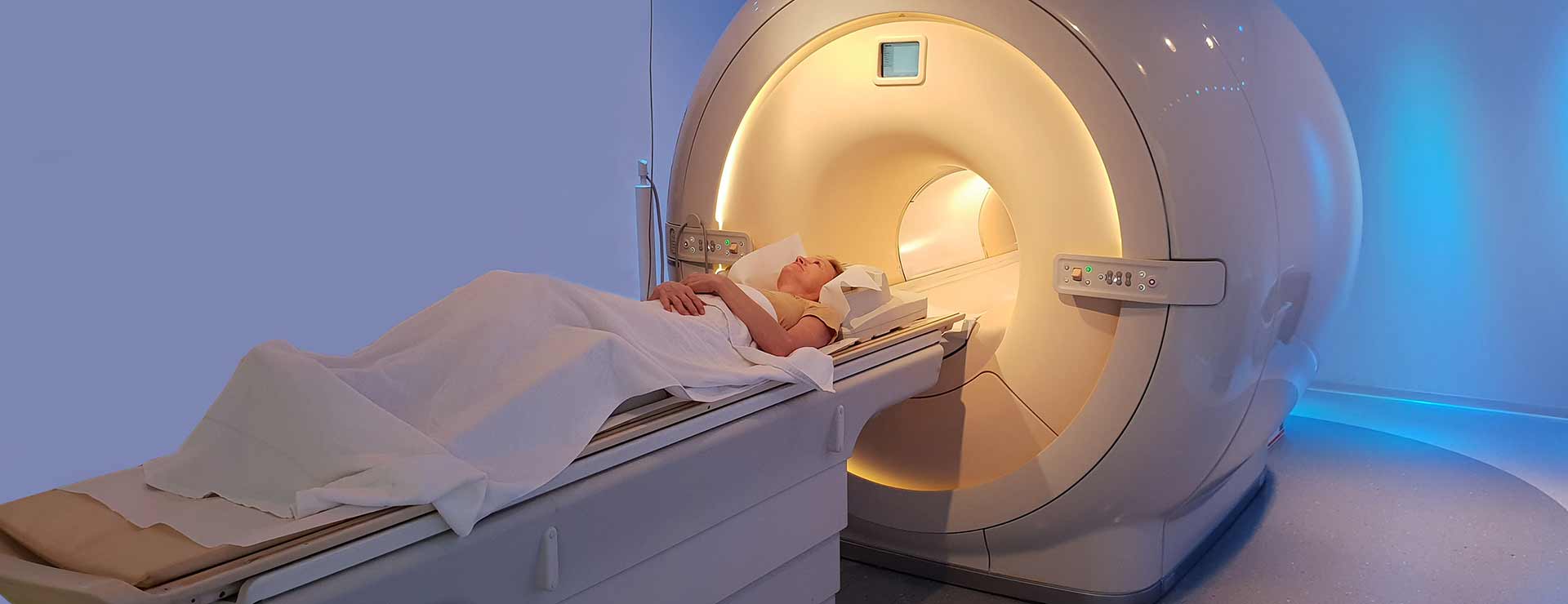
A CT scan of the brain is a non-invasive medical imaging procedure that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the brain. It allows healthcare providers to examine the brain for abnormalities, such as tumors, bleeding, or other conditions.
CT scans provide a more detailed view of the internal structure of the brain. It helps in diagnosing various neurological disorders, including stroke, head trauma, and brain tumors. CT scans are often used to guide surgical procedures and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. 2. How does a CT scan of the brain work?

During a CT scan of the brain, the patient lies down on a table that slides into the CT scanner, which is a large machine shaped like a doughnut. The scanner emits narrow beams of X-rays that pass through the brain from different angles. Detectors inside the scanner measure the X-rays that pass through the brain and transmit the information to a computer. The computer then processes the data to create detailed images of the brain.
CT scanning is painless and typically takes only a few minutes to complete. Contrast dye may be used to enhance the visibility of certain structures or abnormalities. Patients may need to remain still during the scan to ensure clear images. 3. What are the benefits of a CT scan of the brain?
A CT scan of the brain offers several benefits:
It helps diagnose various brain conditions, enabling timely treatment. CT scans are non-invasive and provide quick results. They can be performed in emergency situations to assess head injuries. CT scans are widely available and accessible in most healthcare facilities. 4. Are there any risks associated with a CT scan of the brain?
While CT scans are generally safe, there are a few potential risks:
Exposure to X-ray radiation: Although the amount of radiation is low, it can accumulate over time. The benefits of the scan usually outweigh the potential risks. Allergic reactions: In some cases, contrast dye used during the scan may cause allergic reactions in individuals with specific allergies. Pregnancy concerns: It's important to inform the healthcare provider if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant, as X-rays can potentially harm the developing fetus. 5. How should I prepare for a CT scan of the brain?
Prior to a CT scan of the brain:
Inform your healthcare provider about any allergies or medical conditions. Remove any metal objects, such as jewelry, that may interfere with the scan. Follow fasting instructions if required, especially if a contrast dye will be administered. 6. What can I expect during a CT scan of the brain?
During the procedure:
You will be positioned on a table that slides into the CT scanner. You will need to remain still and follow the instructions provided by the radiology technologist. The scanner may make some buzzing or whirring sounds during the procedure. 7. How long does a CT scan of the brain take?
A CT scan of the brain typically takes about 10 to 15 minutes to complete. However, the duration may vary based on individual circumstances and the complexity of the condition being evaluated.
8. Will a CT scan of the brain cause any discomfort?
No, a CT scan of the brain is a painless procedure. You may be required to lie still and hold your breath for a few seconds during the scan, but it doesn't cause any discomfort.
9. Can I eat or drink before a CT scan of the brain?
In most cases, you can eat and drink normally before a CT scan of the brain, unless your healthcare provider specifically instructs you to fast. However, if a contrast dye is going to be administered, you may be instructed to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan.
10. How soon can I get the results of a CT scan of the brain?
The radiologist will interpret the CT scan images and provide a report to your healthcare provider. The time it takes to receive the results can vary, but it is usually within a few days. Your healthcare provider will discuss the results with you during a follow-up appointment.
11. Can anyone have a CT scan of the brain?
Most people can safely undergo a CT scan of the brain. However, individuals who are pregnant or have certain medical conditions may require special precautions or alternatives. It's essential to discuss your specific situation with your healthcare provider.
12. Are there any alternatives to a CT scan of the brain?
Depending on the specific medical condition, alternatives to a CT scan of the brain may include:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): It uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan: It uses a radioactive tracer to measure metabolic activity in the brain. Ultrasound: It uses sound waves to generate images and is often used in infants and young children. However, the choice of imaging modality depends on the individual case and the information required by the healthcare provider to make an accurate diagnosis.




Comments
Post a Comment